Platforms and Ecosystems
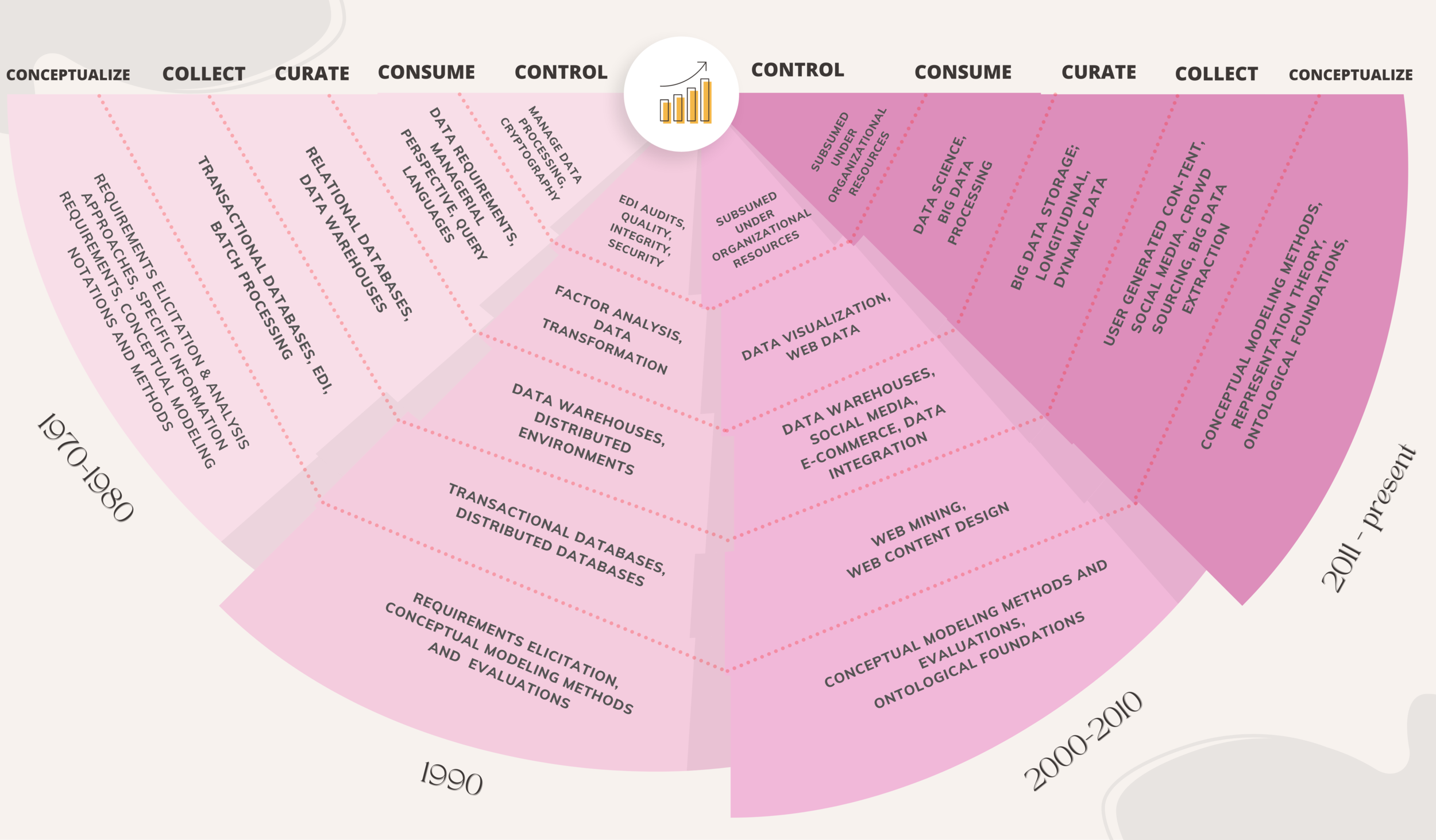
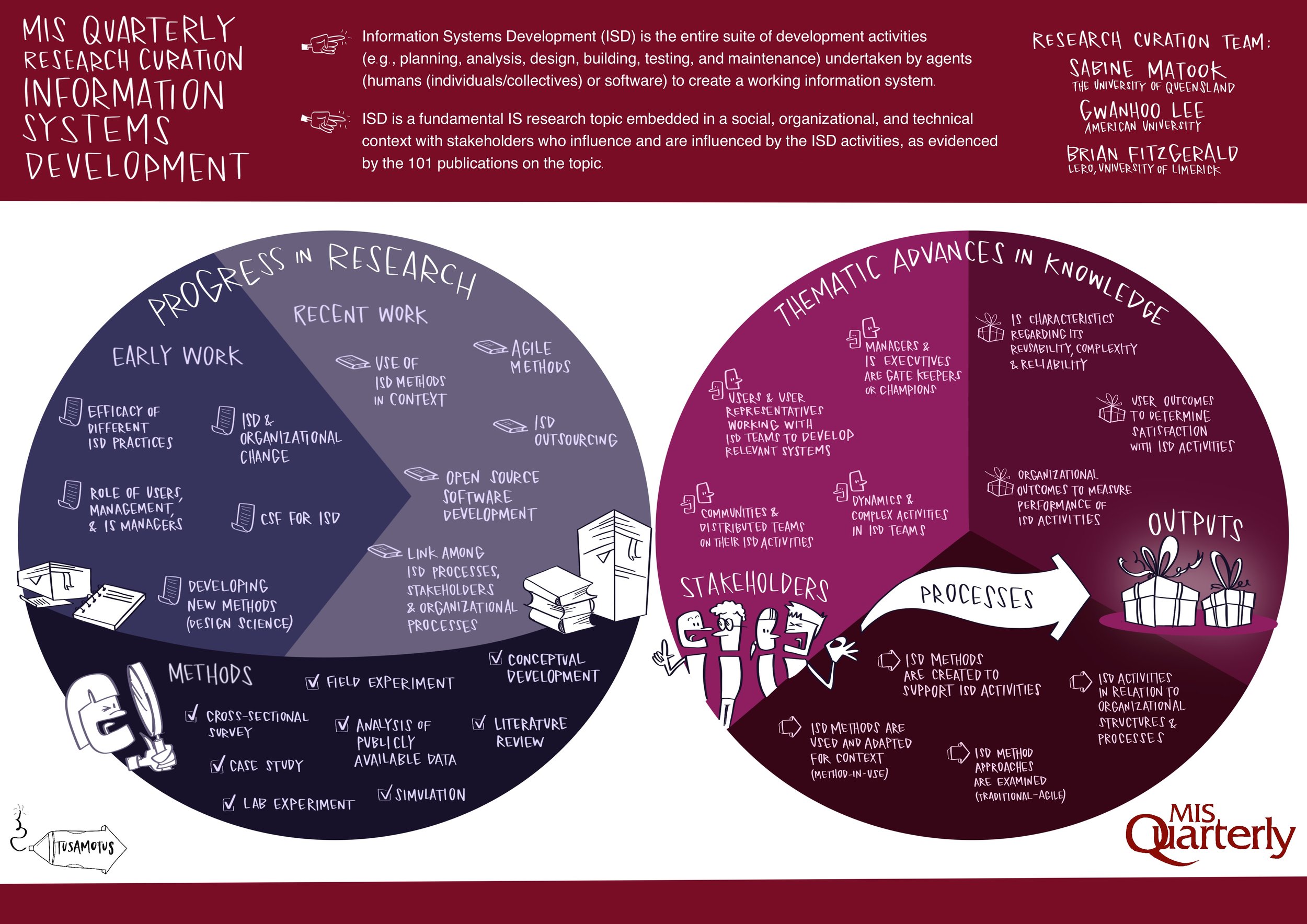
/The success of platforms such as Amazon, Alibaba, Google, Uber, Netflix and Facebook has generated great interest. There is now a large body of research in MIS Quarterly on platforms (and the closely associated concept of ecosystems). This curation brings readers up to date on the nature of research on platforms and ecosystems in MIS Quarterly, the major topics covered, and thematic advances over time.
Read More